The Sumerian civilization, considered one of the world's earliest urban cultures, laid the foundation for complex societal organization. Emerging in Mesopotamia around 4500 BCE, the Sumerians developed a rich tapestry of social, economic, and political structures that shaped their daily lives. The Sumerian social structure was characterized by a hierarchical system that influenced various aspects of their civilization, from governance and religion to trade and labor. Understanding this social framework provides insights into how the Sumerians thrived in such an early stage of human history.
At the top of the Sumerian social hierarchy were the ruling elite, including kings and high priests, who wielded significant power and authority. This ruling class was supported by a complex bureaucracy that managed resources, maintained law and order, and organized large-scale construction projects, such as the iconic ziggurats. Below the elite were various social classes, including artisans, farmers, and laborers, each playing a vital role in sustaining and advancing Sumerian society.
The Sumerian social structure was not only defined by wealth and occupation but also by the roles individuals played in religious practices and community life. The interconnectedness of these social strata contributed to a balanced yet dynamic community that thrived on cooperation and mutual reliance. As we delve deeper into this fascinating topic, we will explore the key components of the Sumerian social structure and how they contributed to the civilization’s longevity and cultural richness.
What Were the Key Classes in the Sumerian Social Structure?
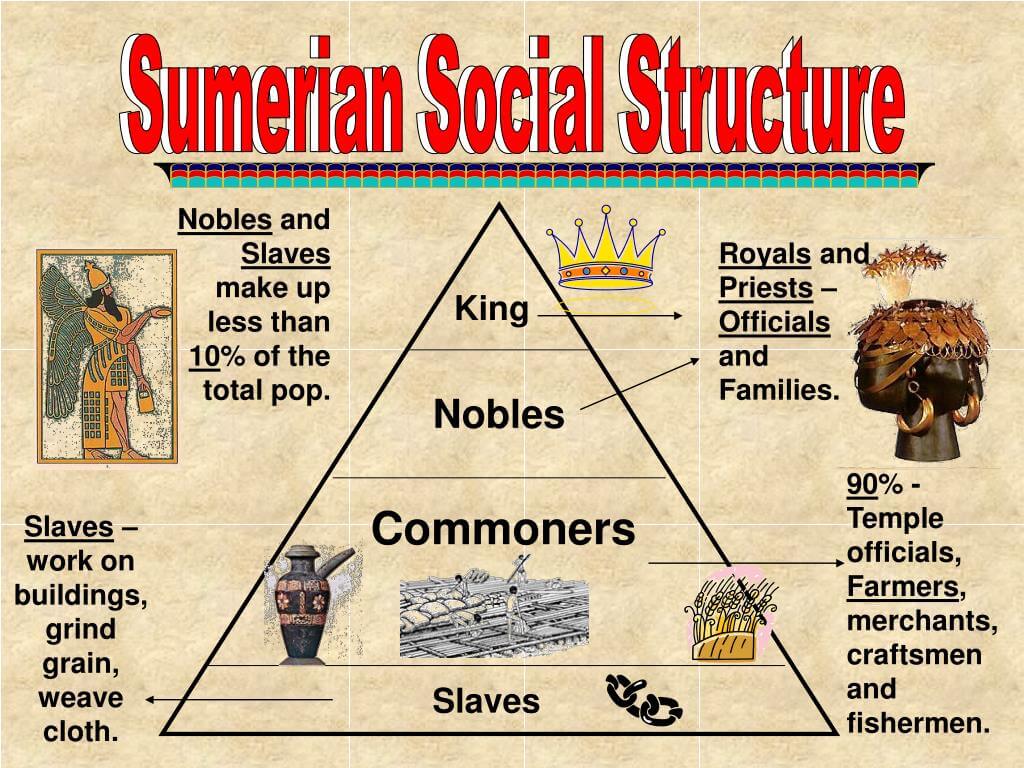
The Sumerian social structure comprised several distinct classes, each with specific roles and responsibilities. Understanding these classes is essential to grasping the overall organization of Sumerian society. The primary social classes included:
- Ruling Class: Kings and priests who held the most power.
- Bureaucrats: Officials who managed the affairs of the state.
- Artisans and Merchants: Skilled craftsmen and traders who contributed to the economy.
- Farmers: The backbone of the Sumerian economy, responsible for food production.
- Laborers: Individuals who performed manual labor, often on construction projects.
- Slaves: People who were captured in warfare or indebted, often working in harsh conditions.
How Did Religion Influence the Sumerian Social Structure?
Religion played a pivotal role in shaping the Sumerian social structure. The Sumerians believed in a pantheon of gods who governed various aspects of life, and the high priests acted as intermediaries between the divine and the people. This connection to the divine reinforced the ruling class's authority, as they were often seen as chosen by the gods to lead and protect the community. Religious institutions were also significant landowners, further consolidating power and wealth among the elite.
What Role Did Gender Play in the Sumerian Social Structure?
Gender roles in Sumerian society were relatively defined, with men generally occupying positions of power and authority. However, women also held important roles within the family and society. Some women became priestesses, gaining significant influence, while others managed households and participated in economic activities. Despite the patriarchal structure, women had legal rights that allowed them to own property and engage in business, showcasing a more complex view of gender within the social hierarchy.
What Were the Economic Implications of the Sumerian Social Structure?
The economic framework of Sumerian society was closely tied to its social structure. The ruling elite controlled vast lands and resources, while farmers and laborers worked to sustain the economy. Trade also played a significant role, with merchants facilitating exchanges not only within Sumer but also with neighboring civilizations. The division of labor allowed for specialization, leading to advancements in agricultural techniques, craftsmanship, and trade practices.
How Did the Sumerian Social Structure Evolve Over Time?
As the Sumerian civilization progressed, its social structure evolved in response to various factors, including warfare, trade, and cultural exchanges. The rise of city-states led to increased competition and the emergence of more complex bureaucratic systems. Additionally, the introduction of new technologies and agricultural practices allowed for population growth, which further impacted the social hierarchy. Over time, the Sumerian social structure became more stratified, with a clearer delineation of roles and responsibilities.
What Legacy Did the Sumerian Social Structure Leave Behind?
The Sumerian social structure laid the groundwork for future civilizations in Mesopotamia and beyond. Its emphasis on organized governance, social roles, and economic interdependence influenced subsequent societies, including the Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. Many of the administrative practices developed by the Sumerians, such as record-keeping and legal codes, have had lasting impacts on governance throughout history.
In Conclusion, What Can We Learn from the Sumerian Social Structure?
Studying the Sumerian social structure provides valuable insights into the complexities of early human civilizations. It highlights the importance of organization, cooperation, and adaptability in the face of challenges. By examining the interactions between different social classes, the influence of religion and gender, and the evolving economic landscape, we gain a deeper understanding of how societies function and thrive. The Sumerians not only shaped their world but also left a legacy that continues to inform our understanding of social organization today.